What Is The Difference Between Cell Division In Plant Cells And Animal Cells
What are the Differences Between Plant Cells and Animal Cells?
Around 1838, an animal physiologist, Theodor Schwann, and a botanist, Matthias Schleiden, put forth the unprecedented work on the concept of cells as the building blocks of all living organisms. From that point forward, prison cell theory has grown into the foundations of modern era biological research without which none of today's discoveries would be possible.
We now know that there are a myriad of unlike cell types, with outstanding capabilities and functions. Regardless of how different all types of cells may be, there are mutual characteristics to all of them, along with established differences as well.
Whether we are looking at multicellular organisms or those containing i single cell, all of them will be manifesting the same features necessary to support life. We volition go over sure similarities and characteristics of the animal and plant cells, in order to gain a better agreement of each. In that context, the concluding few paragraphs we will exist focusing on the chief differences between plant cells and animal cells.
Plant Cells
The size of plant cells normally ranges from ten-100 µm, which is a range that is bigger than fauna cells. The main function of these cells in plants is to behave out the process of photosynthesis via chloroplast which gives them their color. The cells themselves maintain their structure thanks to cellulose that make the walls of the cells. These prison cell walls aren't constitute in cells within the animate being kingdom - we'll look at that in only a chip.
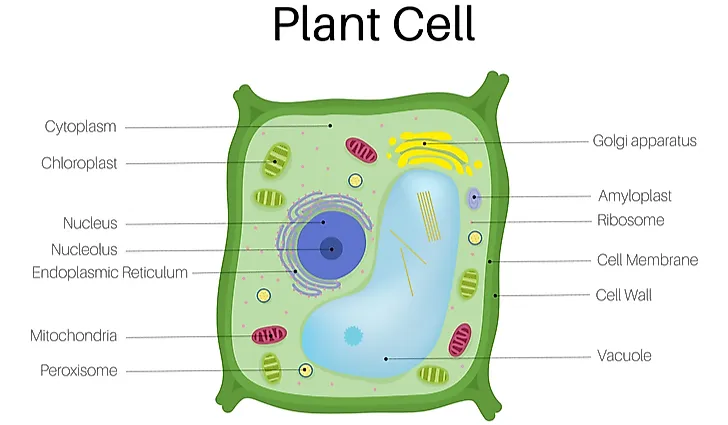
There are several dissimilar small structures within the prison cell itself, called organelles, each with a specific part. These organelles are plant in both types of cells discussed here, with many of them identical in office. Here are some of the most important ones that we observe in plant cells:
Plasma Membrane - makes sure the construction of the cells remains intact and consequently keeps the jail cell content from spilling out. Information technology also enables molecule motion via osmosis and improvidence.
Cell wall - dissimilar from a membrane past being found only in plant cells where it encompasses the cell membrane. The cell wall is firm just completely porous at the same time.
Chloroplasts/plastids - also found only in plant cells, these organelles enable photosynthesis when exposed to sunlight. Plastids are a group name for various kinds of chloroplasts that differ in color.
Vacuoles - provide structural integrity to the cell but also contain a diversity of liquids or solids. These organelles are responsible for the colors we see on flowers.
Cytoplasm - the enzymes establish within these structures are at the captain of all metabolic processes that happen inside.
Fauna Cells
Creature jail cell size ranges from x-xxx µm, which makes it obvious that found cells can be much bigger, clearly, depending on the plant. The chief divergence from plant cells is that creature cells don't contain chloroplast nor structurally important prison cell walls.
It is obvious why animal cells lack in chloroplast, as there is no process of photosynthesis that generates food for the cells - creature cells create their energy via different process. But the interesting question is why exactly do they lack cell walls.
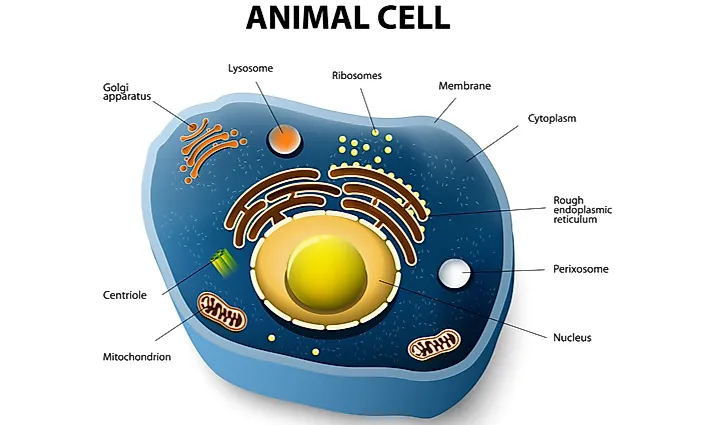
The primary theory is that the master "culprit" for the absence of prison cell wall is the evolution itself. Unlike plants, animal kingdom evolved to have more complex cells that are specialized to a greater extent and are able to sustain the structure of the cell without the cell wall. Obviously, simply like plants cells, they also contain organelles with a diverseness of functions:
Plasma membrane - just like in found cells, this construction allows for molecule movement through the cell itself and protects the internal structures of the cell, that is, other organelles.
Mitochondria - generates the energy necessary to sustain cell life by breaking downwardly nutrients and transforming them into "nutrient" molecules for the cell.
Cytokinesis - responsible for the segmentation of cytoplasm while the jail cell is dividing. In fauna cells, this division happens via the formation of cleavage furrow that grips the membrane and divides it in half.
Centrioles - cylindrically shaped objects inside the cells are agile during the process of prison cell division. Their part is to arrange the formation of microtubules - structural polymers of the cell.
Cilia - microtubules that assist in locomotion of the jail cell.
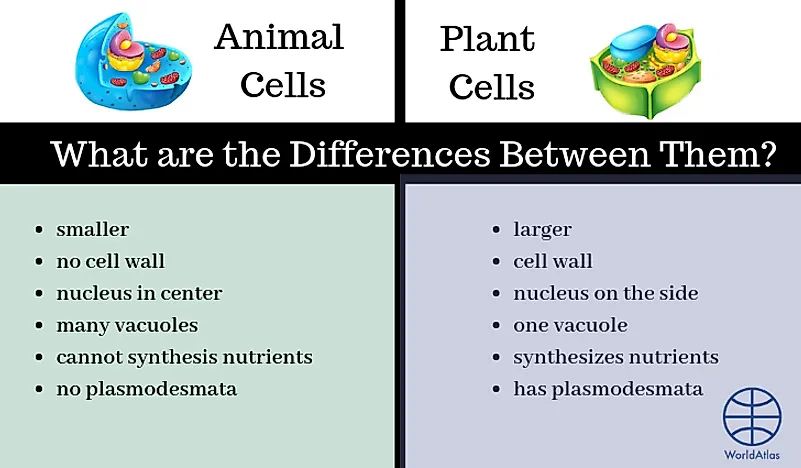
Main Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
Both types of cells are identical in so much that they demand to somehow produce free energy to support themselves and to allow for growth. Both cell types as well contain internal structures that are employed in specific processes that let optimal functioning on a cellular level.
As was visible throughout the commodity, there are certain types of cells that are plant in beast cells that cannot exist found in plant cells, and vice versa.
Dissimilar Organelles
The most obvious ones are cell chloroplast, wall, and vacuoles. These cells can simply be establish in plants. Although both animal and plant kingdom falls nether the eukaryotes (multi-celled, equally opposed to prokaryotic, which is single-celled), animal cells take much more complex construction.
Some organelles that are found in animal cells but non in plant cells are as follows: centrioles, cilia, desmosomes and lysosomes.
Size and Structure
Beast cells wait very different to constitute cells. They are typically smaller than plant cells, with a roundish shape which is fairly irregular. Establish cells accept a rectangular shape and are larger.
The Prison cell Wall
Animal cells do not contain cell walls as one of the organelles, merely they do have a plasma membrane which is the aforementioned equally in plants.
Nucleus Position
Both types of cells practise take a nucleus, which is expected. However, in plants, it is located to the side of the cell, whereas in animal cells have their nucleus in the center.
Number of Vacuoles
Animal cells contain a multitude of small vacuoles, while institute cells can but accommodate one, which is quite large.
Food Synthesis
Animate being cells are not equipped to carry out the synthesis of nutrients, while plants accept no issues with synthesising diverse acids, vitamins and similar.
Lack of Communication Signals
Pores called plasmodesmata are in charge of communication signals, simply as well the passing of molecules between two cells. These pores are not identified in animal cells.
Source: https://www.worldatlas.com/feature/what-are-the-differences-between-plant-cells-and-animal-cells.html
Posted by: richieeverne.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is The Difference Between Cell Division In Plant Cells And Animal Cells"
Post a Comment